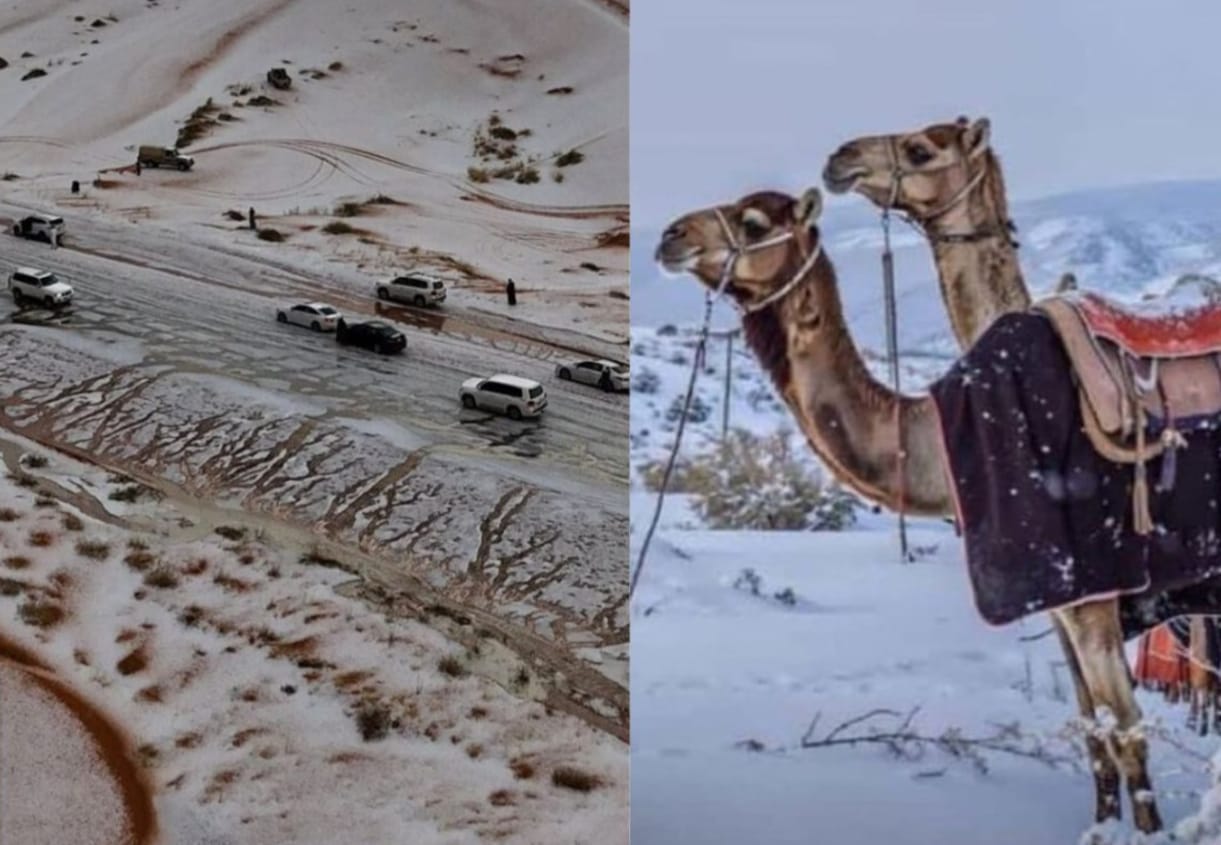
Snowfall, Rain, and Gusty Winds in Saudi Arabia: A Rare Climate Event and Its Wider Environmental Impacts
In recent years, Saudi Arabia has witnessed unusual weather conditions that stand in striking contrast to its reputation for relentless heat, vast deserts, and prolonged dry spells. Episodes of snowfall combined with rainfall and gusty winds—particularly in regions like Tabuk, Al-Jawf, the northern border areas, and even parts of Medina’s highlands—have drawn global attention. While such events have occurred occasionally in the past, their frequency and intensity have noticeably increased in the past decade. This shift is not merely a weather anomaly; it is a reflection of broader climatic changes unfolding across the globe.
This article explores the atmospheric reasons behind this rare phenomenon, the direct effects on Saudi Arabia’s environment, and the larger implications for the Earth’s climate system.
Unusual Weather Patterns: Why Saudi Arabia Is Getting Snow and Strong Winds
Saudi Arabia lies in a geographical zone dominated by hot desert climates, characterized by high temperatures, low humidity, and minimal precipitation. Snowfall is typically limited to high-altitude regions like Jabal al-Lawz near Tabuk. However, recent climatic episodes have featured something more dramatic: a combination of snowfall, heavy rainfall, and gusty winds, often occurring simultaneously.
1. Interaction of Cold Fronts and Warm Air Masses
During winter, cold air masses from Eastern Europe and Siberia sometimes travel southward. When these frigid winds meet the relatively warmer and moist air over the Arabian Peninsula, conditions become favorable for snow formation. The moisture from the Red Sea and Mediterranean enhances rainfall, while the collision of warm and cold air produces turbulence—resulting in strong, gusty winds.
2. Increased Atmospheric Instability
Climate scientists have observed heightened atmospheric instability in the region. This instability encourages more intense storms, unusual rainfall patterns, and sudden temperature drops. These dynamics explain why temperature fluctuations in Saudi Arabia can swing rapidly within a few hours, making snowfall possible in a desert region.
3. Possible Link to Climate Change
While no single event can be directly attributed to climate change, the overall increase in extreme and unseasonal weather patterns is consistent with trends associated with global warming. As the Earth’s temperature changes, the behaviour of jet streams, air masses, and oceanic circulations also shifts, leading to unusual weather in regions that typically maintain stable climates.
Local Environmental Effects in Saudi Arabia
The combination of snowfall, rainfall, and gusty winds brings both benefits and challenges to Saudi Arabia’s environment, infrastructure, and communities.
1. Increased Soil Moisture and Temporary Relief from Drought
Deserts rarely receive meaningful precipitation, but these rare storms help recharge shallow aquifers and improve soil moisture. For agriculture-dependent communities—particularly in northern provinces—this precipitation can bring short-term relief from drought conditions.
However, heavy rain on dry, compact soil often leads to limited absorption, causing surface runoff and flash floods.
2. Risk of Flash Flooding
One of the most immediate threats during such weather events is flooding. Cities like Jeddah and Riyadh have experienced damaging floods in the past due to inadequate drainage systems. When snowfall melts rapidly or rain falls in large volumes, the desert landscape cannot absorb the water quickly. As a result, wadis (dry riverbeds) overflow, leading to hazardous situations for residents and travellers.
3. Impact on Wildlife and Vegetation
Saudi Arabia’s desert ecosystems are adapted to harsh, dry climates. Sudden temperature drops, snow accumulation, and strong winds can create stress for native species.
Some reptiles and desert mammals struggle to regulate body temperatures.
Migratory birds may seek temporary shelter or alter flight routes.
Certain desert plants benefit from increased moisture but may suffer from frost damage.
These disruptions may seem small but can ripple across ecosystems, affecting food chains and breeding cycles.
4. Transportation Disruptions
Heavy winds and snowfall reduce visibility, leading to road accidents and transport delays. Airports in northern Saudi Arabia occasionally suspend flights during such weather, and highways can become temporarily closed. This affects not only residents but also supply chains and tourism, particularly during peak pilgrimage seasons.
5. Strain on Infrastructure
Saudi Arabia’s infrastructure is built primarily for hot climates. Sudden exposure to cold temperatures and moisture can cause:
Cracking in roads
Electrical faults
Damage to lightweight structures
Disruption of communication towers due to storms
These challenges highlight the need for adapting construction practices to more unpredictable weather.

Broader Environmental Effects on Earth
Saudi Arabia’s unusual weather is not an isolated event—it is part of a global pattern of increasingly erratic climate behaviour.
1. Sign of Shifting Climate Zones
As global temperatures rise, climate zones are slowly shifting. Regions that historically remained hot year-round are now experiencing temperature drops in winter that allow rare snowfall. Conversely, regions known for cold and snow are seeing warmer winters. This shifting pattern is a clear indicator of climate adjustment.
2. Influence on Global Atmospheric Circulation
Events like Saudi snowfall contribute to broader atmospheric changes in several ways:
Alteration in wind patterns
Changes in moisture distribution
Modification of high-pressure and low-pressure systems
Such shifts can influence rainfall patterns in Africa, the Mediterranean, and even parts of Asia.
3. Reflection of Increased Weather Extremities Worldwide
Across the world, we are seeing frequent episodes of extremes:
Heatwaves in Europe
Heavy snow in regions unaccustomed to it
Storms and cyclones gaining strength
Droughts extending longer
These patterns reaffirm scientists’ warnings that the Earth’s climate system is becoming increasingly unstable.
4. Contribution to Global Awareness
While unusual weather often causes inconvenience, it also increases public awareness about climate change. Such highly visible events prompt governments and communities to reflect on:
Sustainable development
Better disaster preparedness
Improved climate research
Renewable energy adoption
Saudi Arabia, for instance, has accelerated its Vision 2030 initiatives focusing on environmental protection partly due to such climate irregularities.
Conclusion
Snowfall accompanied by rain and gusty winds in Saudi Arabia is a dramatic reminder that no region of the world is immune to climate variability. This rare weather phenomenon highlights both the beauty and fragility of the Earth’s climate system. While it offers temporary environmental benefits like improved moisture, it also presents challenges—from flash floods to ecosystem disruptions. More importantly, it serves as a small piece in the larger puzzle of global climate change, urging humanity to understand, adapt, and mitigate the long-term effects of environmental shifts.